CellCommuNet
Version: 1.0
Welcome to CellCommuNet
An atlas of cell–cell communication networks from single-cell RNA sequencing data of human and mouse tissues in normal and disease states.
Cell‒cell communication, as a basic feature of multicellular organisms, is crucial for maintaining the biological functions and microenvironmental homeostasis of cells, organs, and whole organisms. Alterations in cell‒cell communication contribute to many diseases, including cancers. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) provides a powerful method for studying cell‒cell communication by analysing ligand‒receptor interactions.
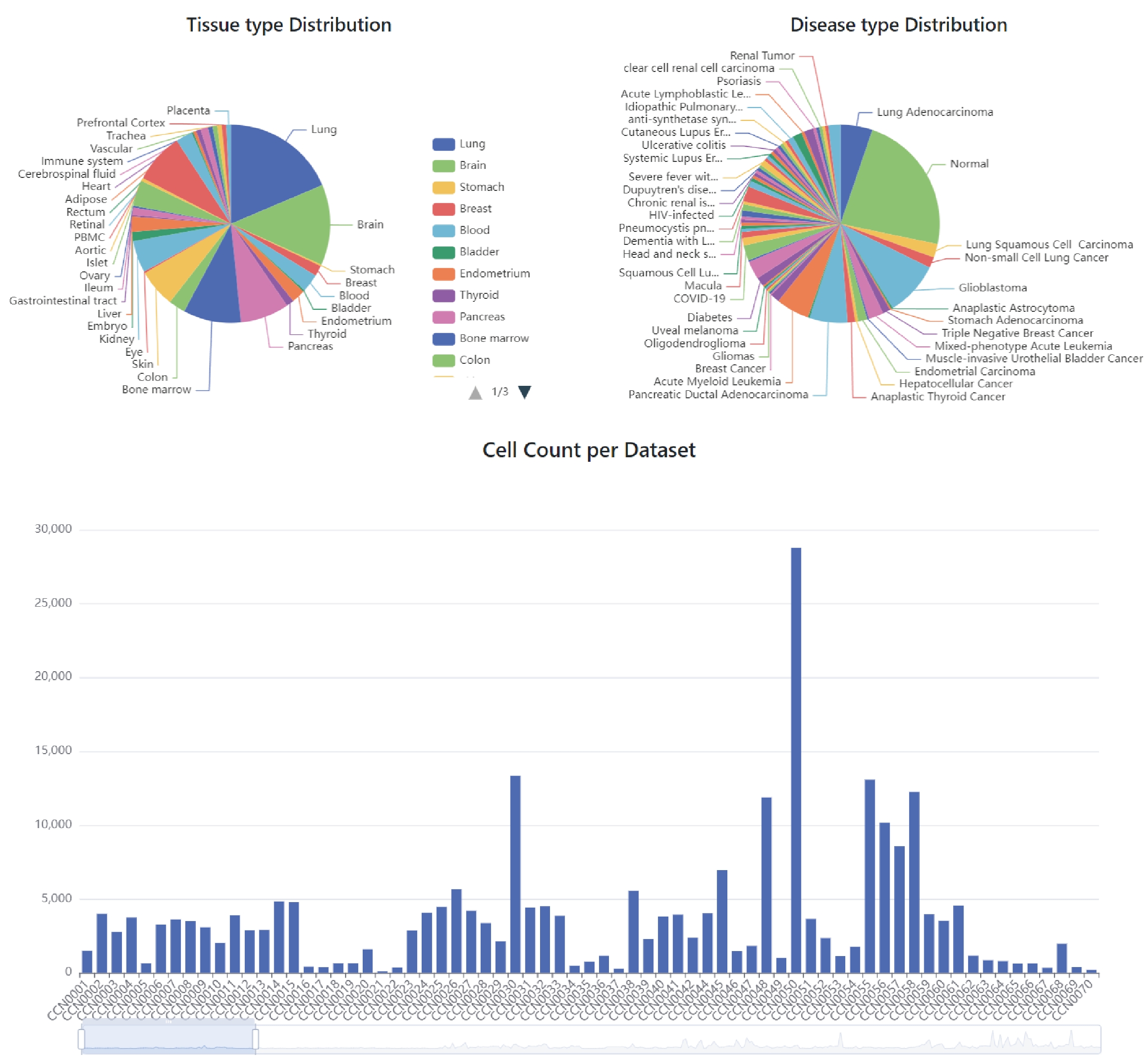
Here, we have constructed CellCommuNet to present the results of cell‒cell communication analysis between cells in various diseases. We collected and curated 376 scRNAseq datasets with over 4,300,000 cell transcriptomics, covering healthy samples and a wide range of diseases. Additionally, we organized 118 comparison datasets between disease and control samples from the same scRNAseq study. Furthermore, we used Seurat/ScType/Cellmarker/CellChat tools for cell communication analysis. As a result, 514,463 cell‒cell communication networks of each ligand-receptor pair and each signaling pathway were inferred, and 329,174 of those networks shows difference between disease and healthy group. We finally deposited the cell‒cell communication networks into CellCommuNet.
| No. of disease types | 82 |
| No. of tissue types | 35 |
| No. of single datasets | 376 |
| No. of comparison datasets | 118 |
| No. of total communications | 514,463 |
| No. of differential communications | 329,174 |
| No. of cell counts | 4,327,804 |
| No. of cell types | 397 |
| Data were updated. | [2023-09-01] |
| CellCommuNet 1.0 was released. | [2023-06-17] |
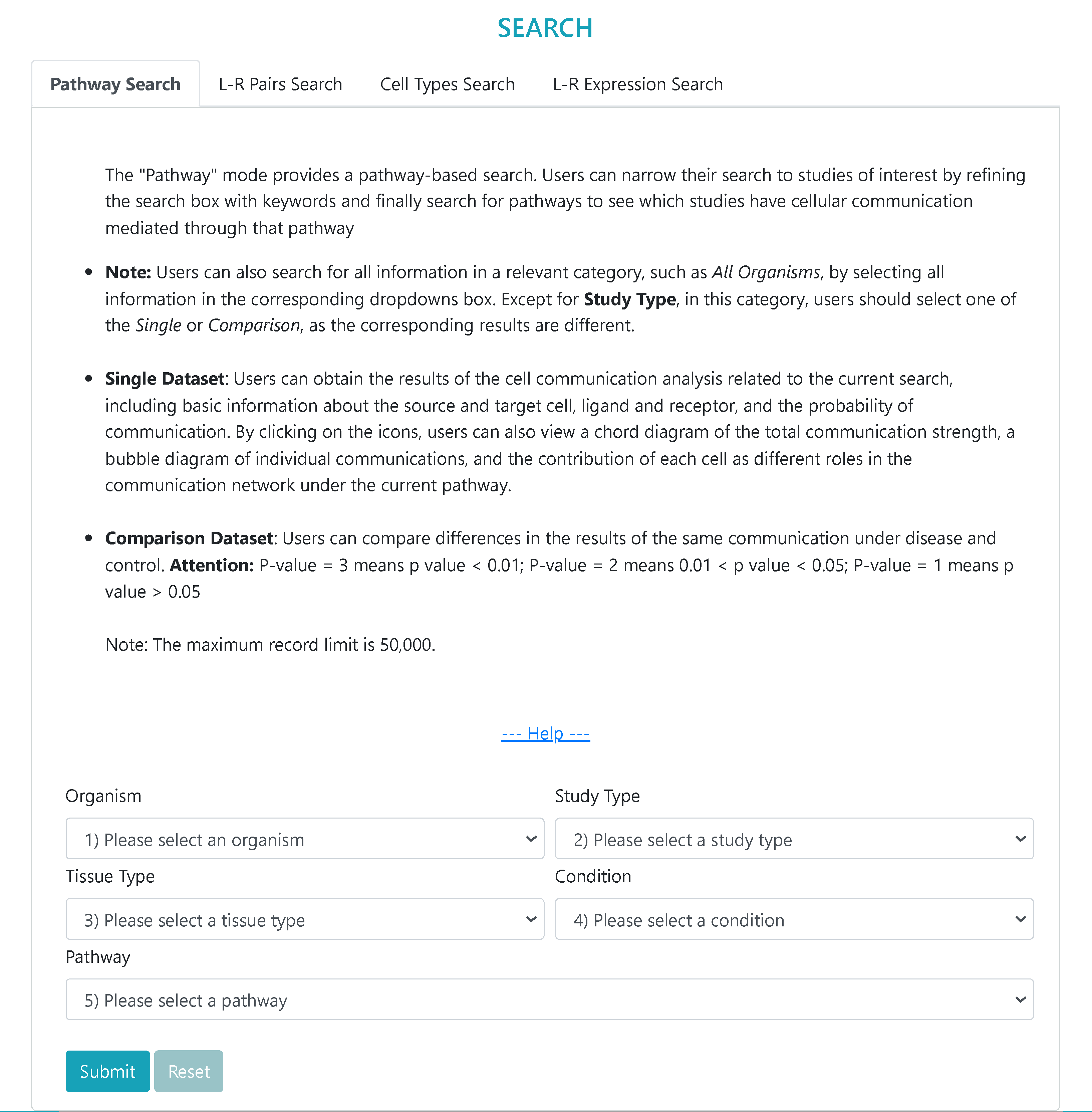
> Users can easily “SEARCH” the results of cell communication analysis in a particular study from four modes, i.e., pathways, ligand‒receptor pairs, cell types and ligand-receptor gene expression.
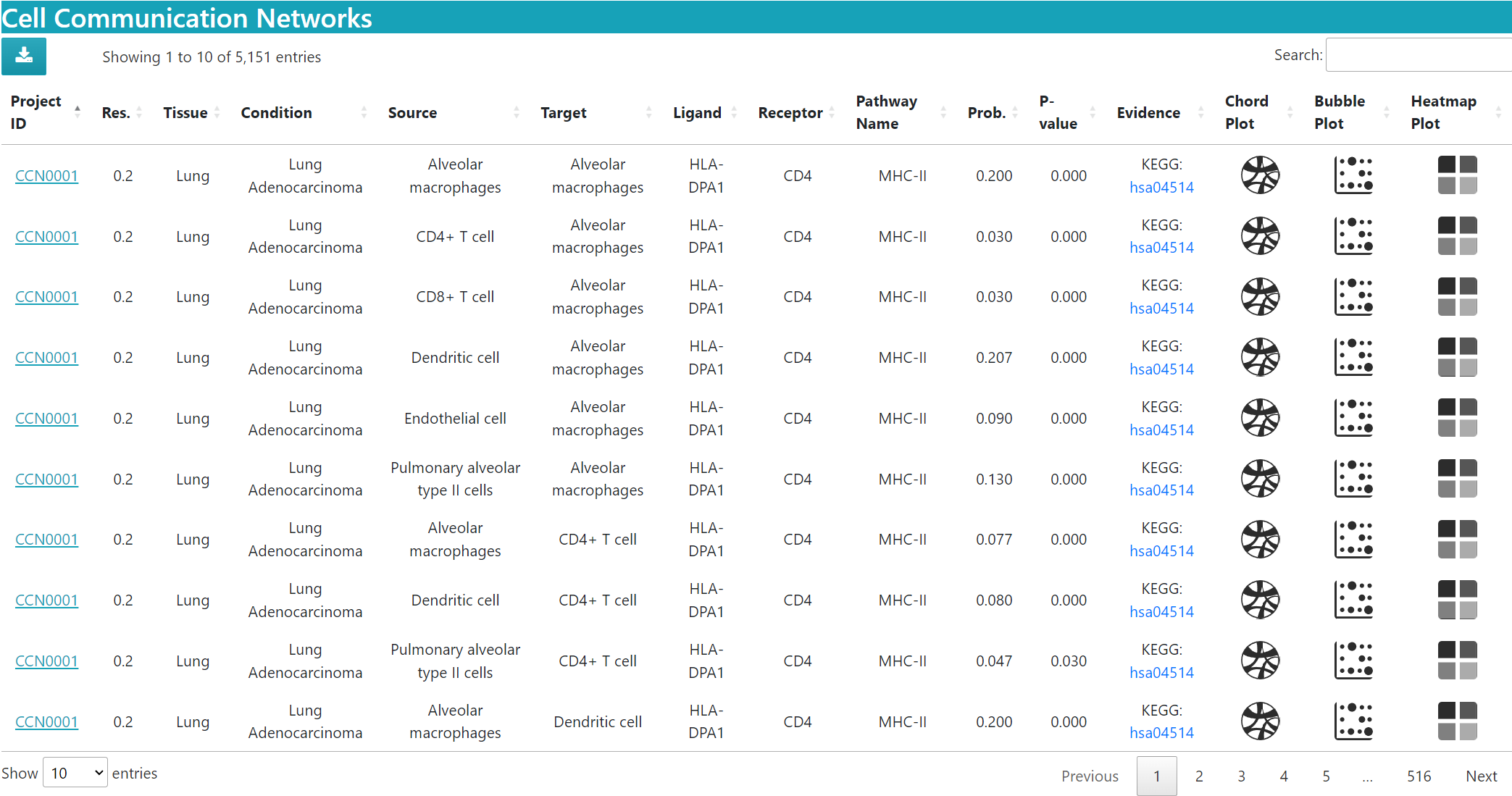
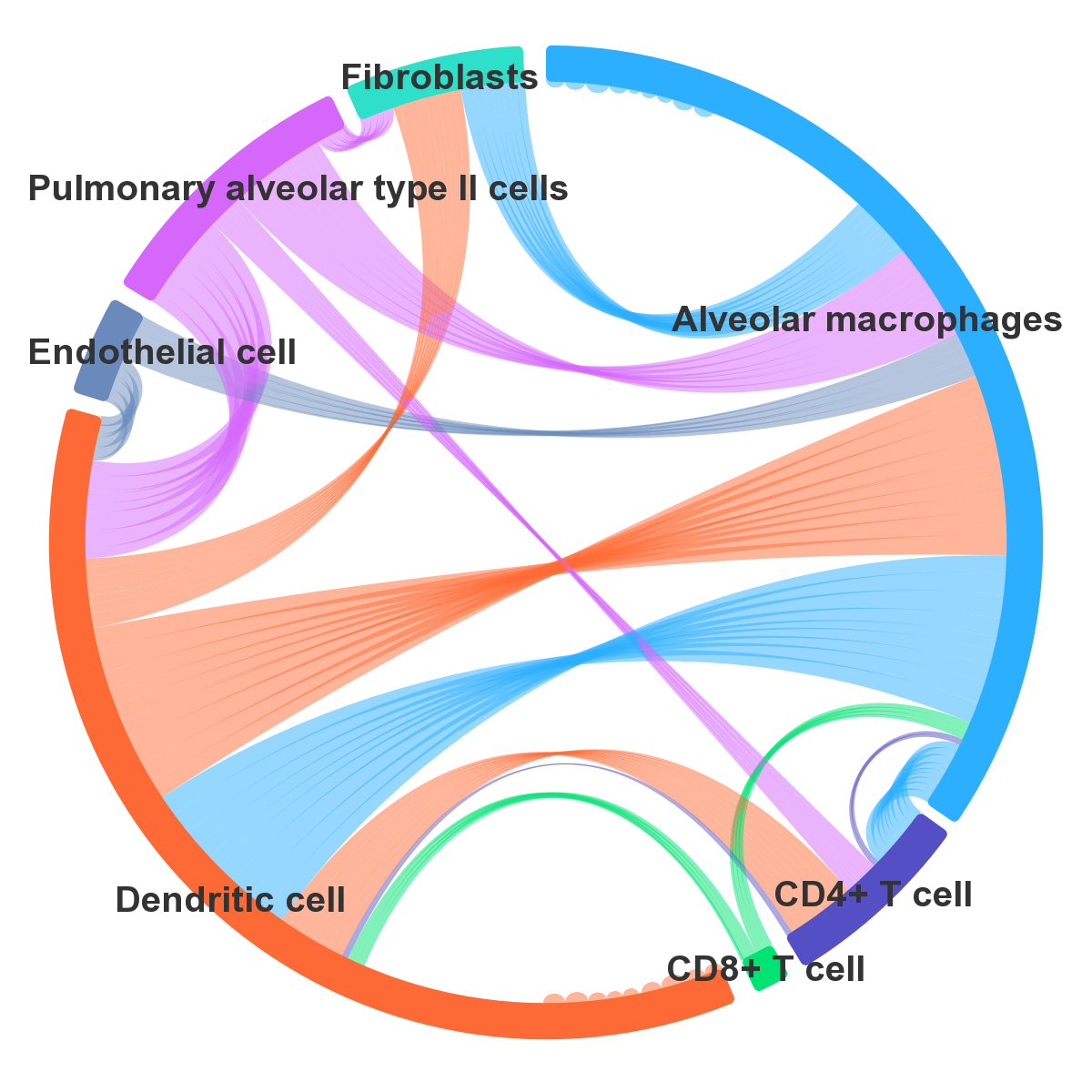
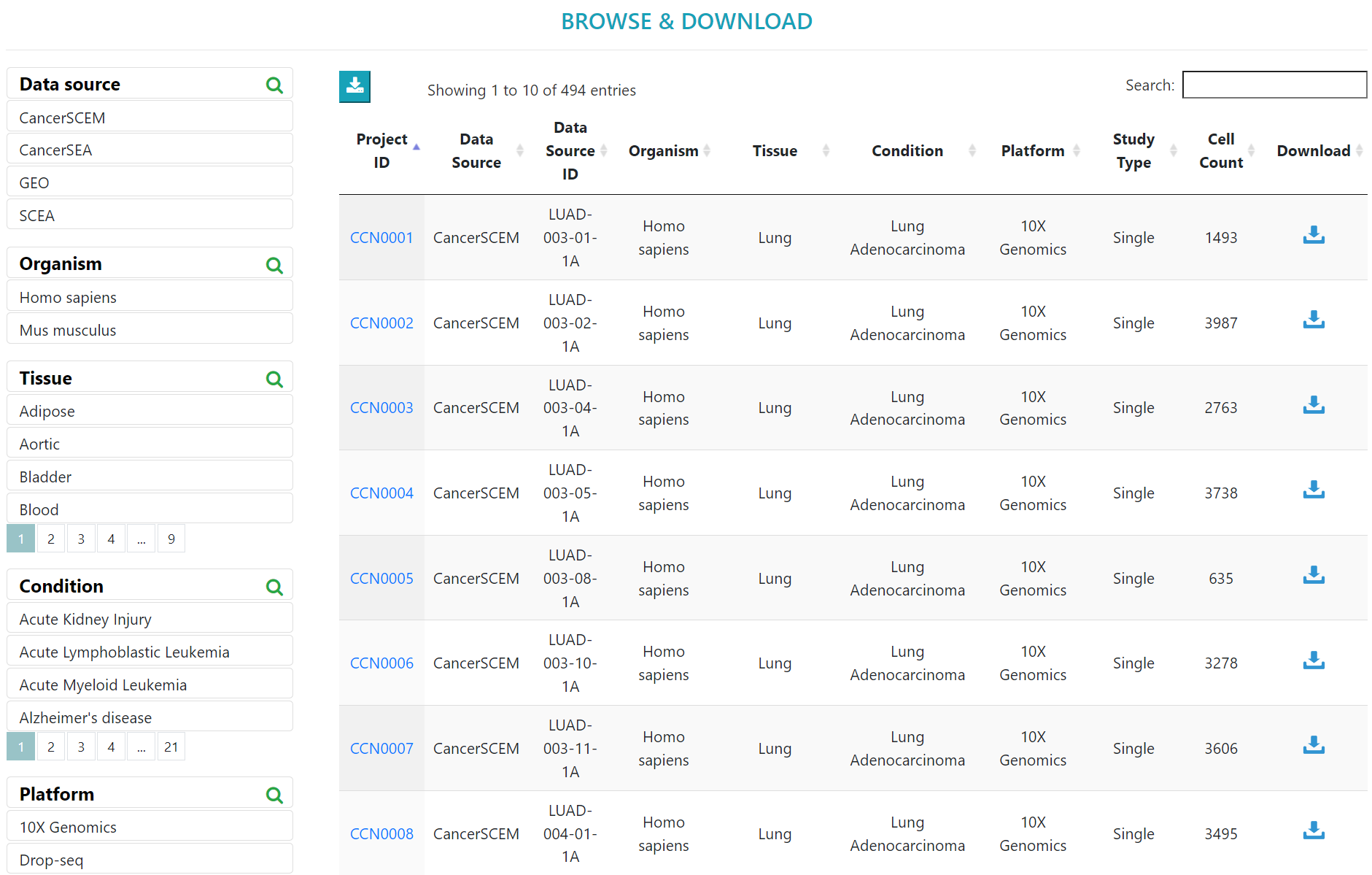
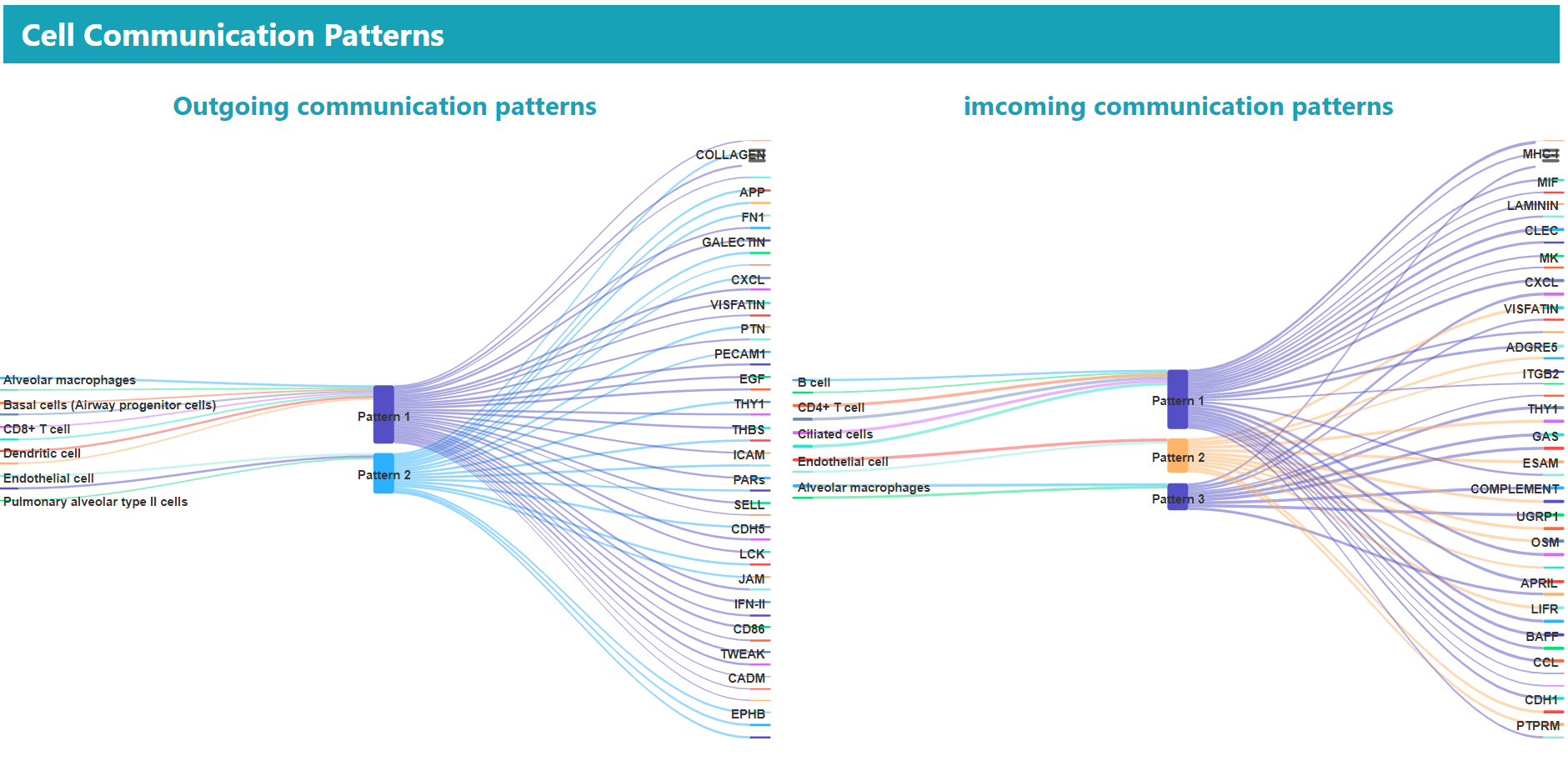
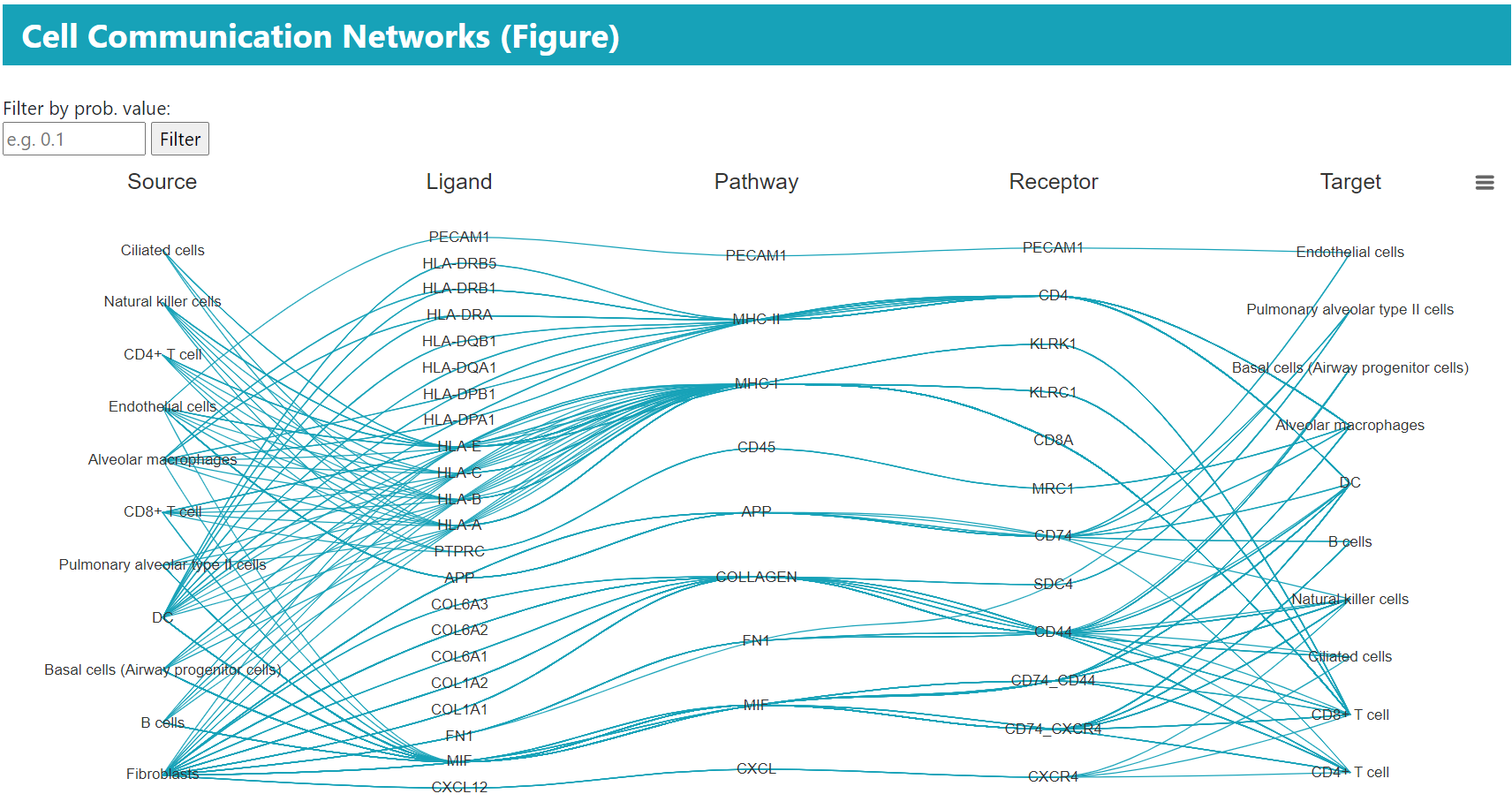
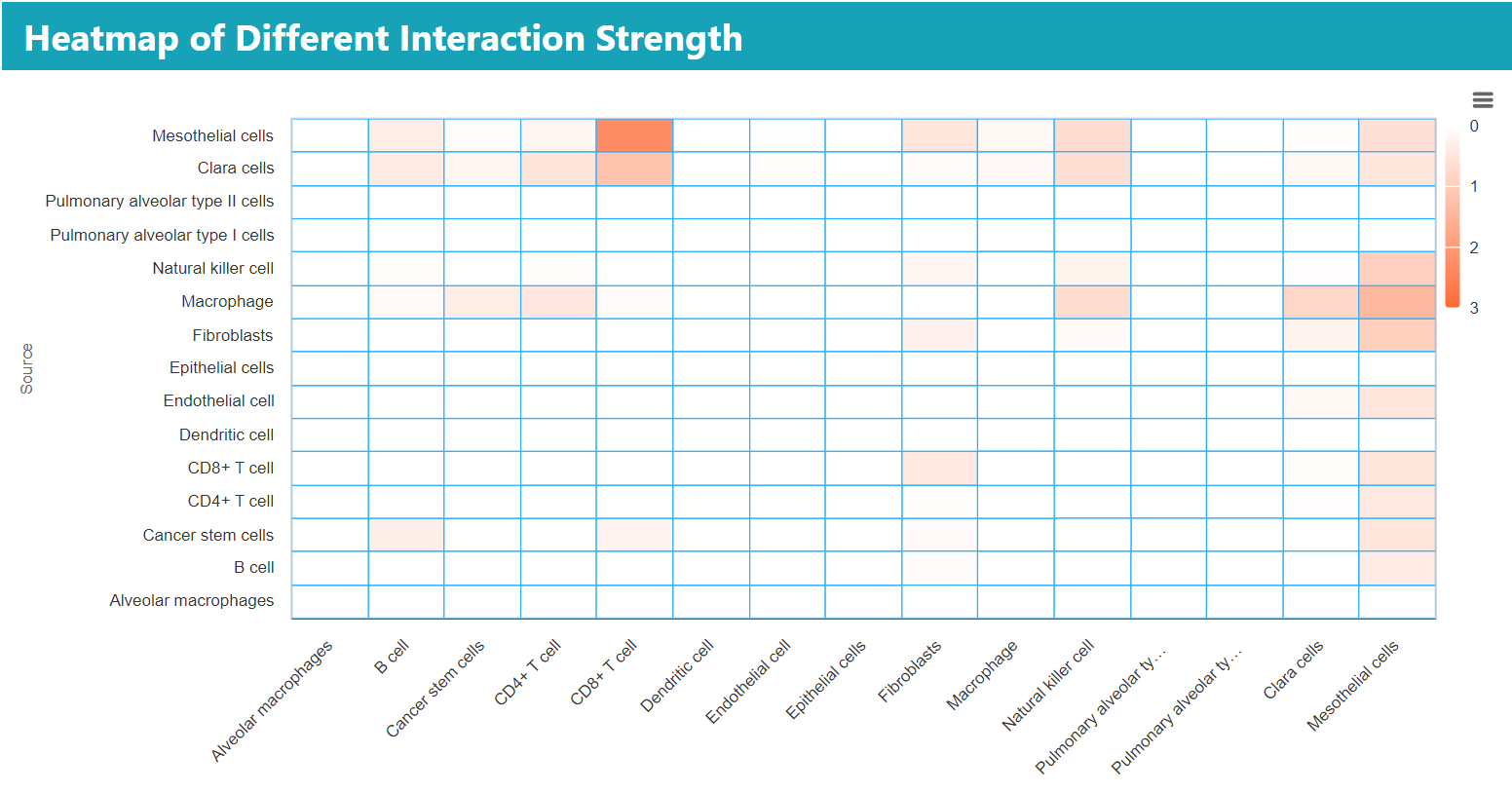
> In the “BROWSE & DOWNLOAD” section, users can view the detailed results of the cell communication analysis for each dataset, including cell communication strength, outgoing and incoming signal pattern.
> Users can query differences in the strength of cell‒cell communication signals and changes in relative information flow between disease and normal samples
> In brief, CellCommuNet presents cell‒cell communication analysis results for tissues in various states in an interactive graphical format, and allows the differential analysis of communication strength between disease and normal samples.